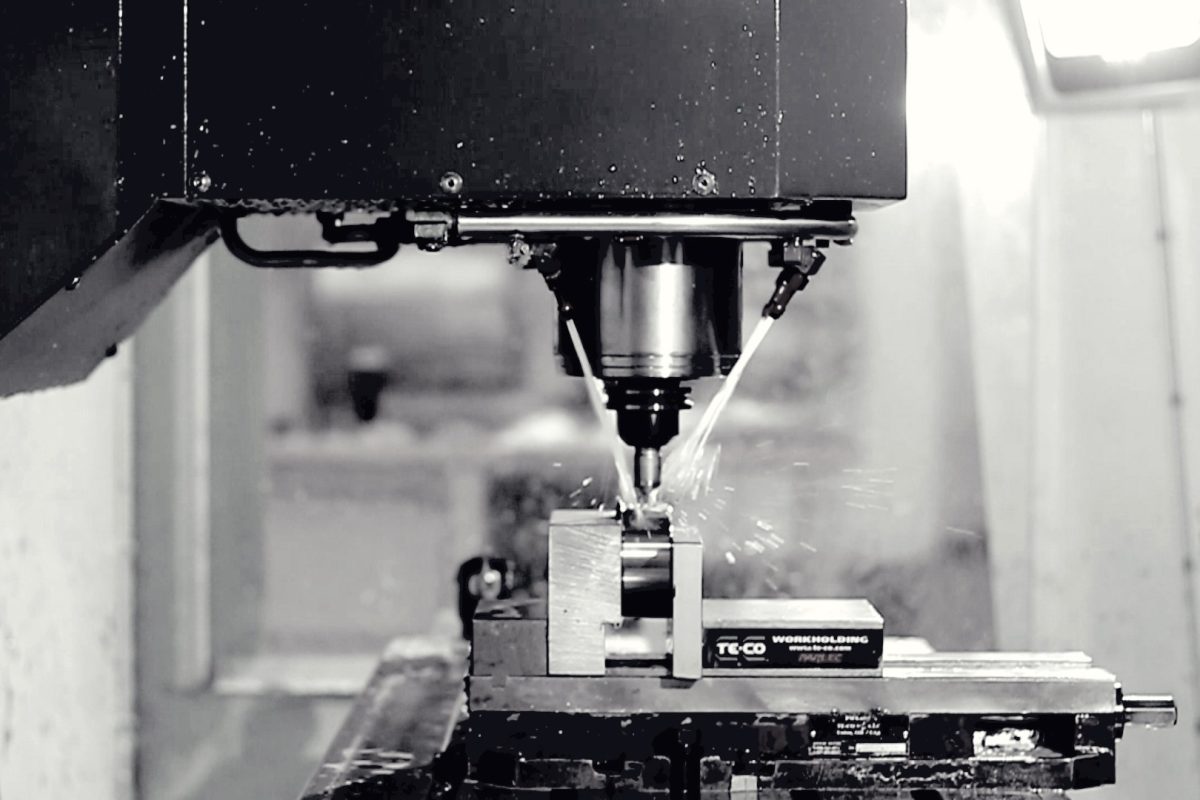
CNC Milling
At a Glance
Lifecycle
Lead Time
Materials
Tolerance
About the Process
If your part is any sort of shape other than cylindrical, or lacks rotational symmetry about some imaginary axis through the part body, then a CNC mill is likely the machine for you. With milling, the stock that the part will be cut from is usually a six-sided bar or sheet of material (though it can also be a cylindrical rod). This stock is fixtured to the bed of the machine and the features of the part are cut using a rotating tool such as a drill or endmill.
With a 3-axis machine, the rotating tool mentioned above can translate relative to the part in the X, Y, and Z axes (thus the name), but is fixed in a vertical (or horizontal, depending on the machine) orientation. With modern CNC mills, the tool can also move in any combination of the 3 axes simultaneously.
A 5-axis machine is capable of the same movements as a 3-axis machine, but with added rotation about the X and Y axes. It is usually the bed that rotates rather than the toolhead, though both types of machines do exist. This added rotation allows for much more freedom when machining each setup.

Materials
Plastics

ABS
A low-cost engineering plastic widely used for
pre-injection molding prototypes. CNC machined
ABS is a great option for production-like parts
where detail and mechanical properties are important.

Polycarbonate
PC is one of the most common plastics used in
manufacturing. Famous examples of the material
are first generation MacBook laptops, safety goggles,
and optical disks.
Polycarbonate is heat-resistant, impact-resistant, flame-
retardant, and one of the most recycled plastics in the world.

PMMA (Acrylic)
Acrylic is a scratch-resistant plastic, available optically
clear or opaque. It is often used for tanks, panels,
and optical applications. It can be somewhat brittle in
thin walled areas, so it is not recommended for delicate or
complex geometries.
This plastic is also known as PMMA, an abbreviation
of its full chemical name, polymethyl methacrylate
as well as by the trade names Plexiglas and Lucite.

Nylon
Nylon 6/6 is the most commonly used of the Nylon
family of plastics. It enjoys relatively high chemical
and heat resistance, and is stiff enough to retain
its shape, but tough enough not to permanently
deform under load.
Two of the most notable use cases for Nylon
are in medical devices and electronics insulation,
notably screws and spacers for panel mounted
circuit boards.

Nylon GF
Glass reinforced Nylon material for performance parts
requiring high stiffness and low abrasive wear.

PEEK
A high-performance engineering plastic with outstanding
resistance to harsh chemicals, and excellent mechanical
strength and dimensional stability. Suitable for
continuous use at temperatures up to 170C

Ultem
A material which is extremely strong and stiff with
high dielectric strength. Resistant to hydrolysis
when exposed to hot water and steam

Delrin
Delrin (generic: acetal) is a low-friction, high-stiffness
material. It is used in applications ranging from auto
parts to musical instruments. With a relatively high
toughness and minimal elongation, Delrin boasts excellent
dimensional accuracy.
HDPE
HDPE is a naturally opaque white because of its
crystalline structure, but is also available dyed
black in more limited stock sizes. It has a
waxy finish leveraged for low-friction applications.
It is also an excellent electrical insulator as well as being
moisture and chemically-resistant.
PP
Polypropylene (PP) resists most solvents and chemicals,
which makes it a wonderful material to manufacture
laboratory equipment and containers for a variety of
applications. PP also offers good fatigue strength.
Materials
Metals

Aluminium
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used metals in
the world because of its excellent strength-to-weight
ratio, low cost, and recyclability. Shapefy offers
Our standard alloy on platform is 6061, a versatile
and easy-to-machine metal. It is corrosion-resistant,
non-magnetic, and heat treatable.
7075 Aluminum is a hard, high strength alternative
to 6061 Aluminum. It is often used for parts in
high-stress applications, and is also corrosion-resistant,
non-magnetic and heat treatable.
Also known as jig plate or cast tool, MIC6 is a cast
aluminum alloy that is great for tight tolerance
applications due to it being stress-relieved. It is most
commonly used in precision machine tables and tooling.
MIC6 is non-magnetic and not heat treatable.

Brass
360 Brass is also known as free machining brass,
due to it having the highest amount of lead content of
any brass alloy. This excellent machinability comes with
minimal tool wear. It is commonly used for a variety
of parts such as gears, lock components, pipe
fittings, and ornamental applications.

Copper
Copper has a shiny reddish-orange finish, which
varies slightly based on the surface finish method.
Offers excellent thermal and electrical conductivity.
Available in 110 and 101 Alloys.

Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and rust,
making it suitable for situations where a part
may be exposed to the elements for long period of time.
Stainless steel is also fairly malleable and ductile.
Good for industrial applications, fittings, fasteners,
cookware, medical devices.
making it suitable for situations where a part
may be exposed to the elements for long period of time.
Stainless steel is also fairly malleable and ductile.
Good for industrial applications, fittings, fasteners,
cookware, medical devices.

Steel
1018 Steel is a mild, low carbon steel that is machinable,
weldable and useful where high-strength is not
required, such as fixtures and mounting plates. It is
magnetic and heat treatable.
4140 alloy steel is generally harder and stronger than
carbon steel. Additionally, it provides high impact
resistance, fatigue strength, and torsional strength
which makes 4140 a great choice for drive shafts,
axles, and torsion bars. In terms of hardening,
4140 can be hardened using a variety of methods
such as cold working, or heating and quenching.
weldable and useful where high-strength is not
required, such as fixtures and mounting plates. It is
magnetic and heat treatable.
4140 alloy steel is generally harder and stronger than
carbon steel. Additionally, it provides high impact
resistance, fatigue strength, and torsional strength
which makes 4140 a great choice for drive shafts,
axles, and torsion bars. In terms of hardening,
4140 can be hardened using a variety of methods
such as cold working, or heating and quenching.

Titanium
Titanium’s properties, which are a combination of high
strength, stiffness, toughness, low density, and good
corrosion resistance provided by various titanium
alloys at very low to elevated temperatures, allow
weight savings in aerospace structures and other
high-performance applications.
Titanium is a low-density element (approximately 60%
of the density of iron) that can be strengthened by
alloying and deformation processing. Titanium is
nonmagnetic and has good heat-transfer properties.
Surface Finishes
Surface finishes are applied after machining and can change the appearance, surface roughness, hardness and chemical resistance of the produced parts.This way aesthetic needs or technical requirements can be achieved.
Name
Description
Design Recommendations
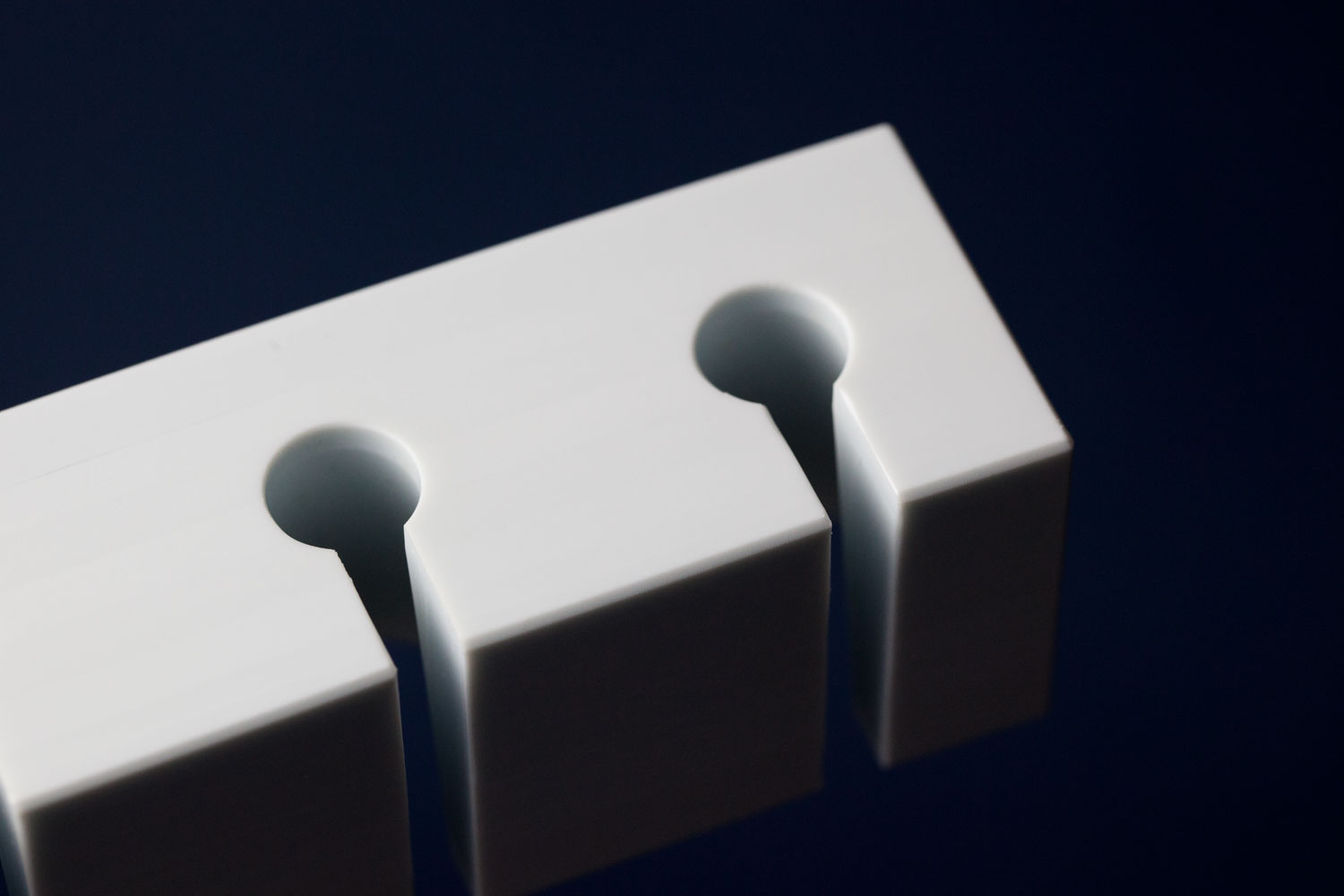
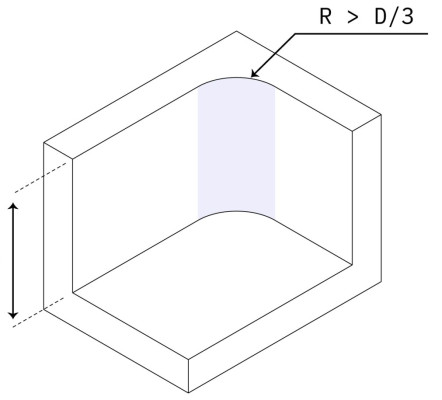
Internal Radius
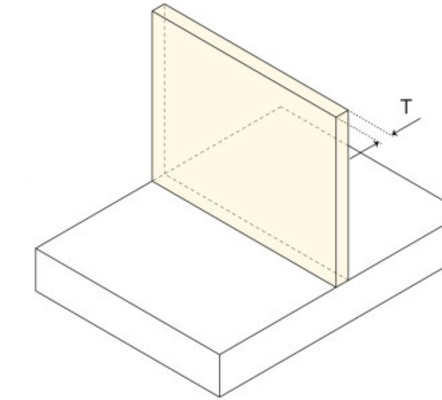
Wall thickness
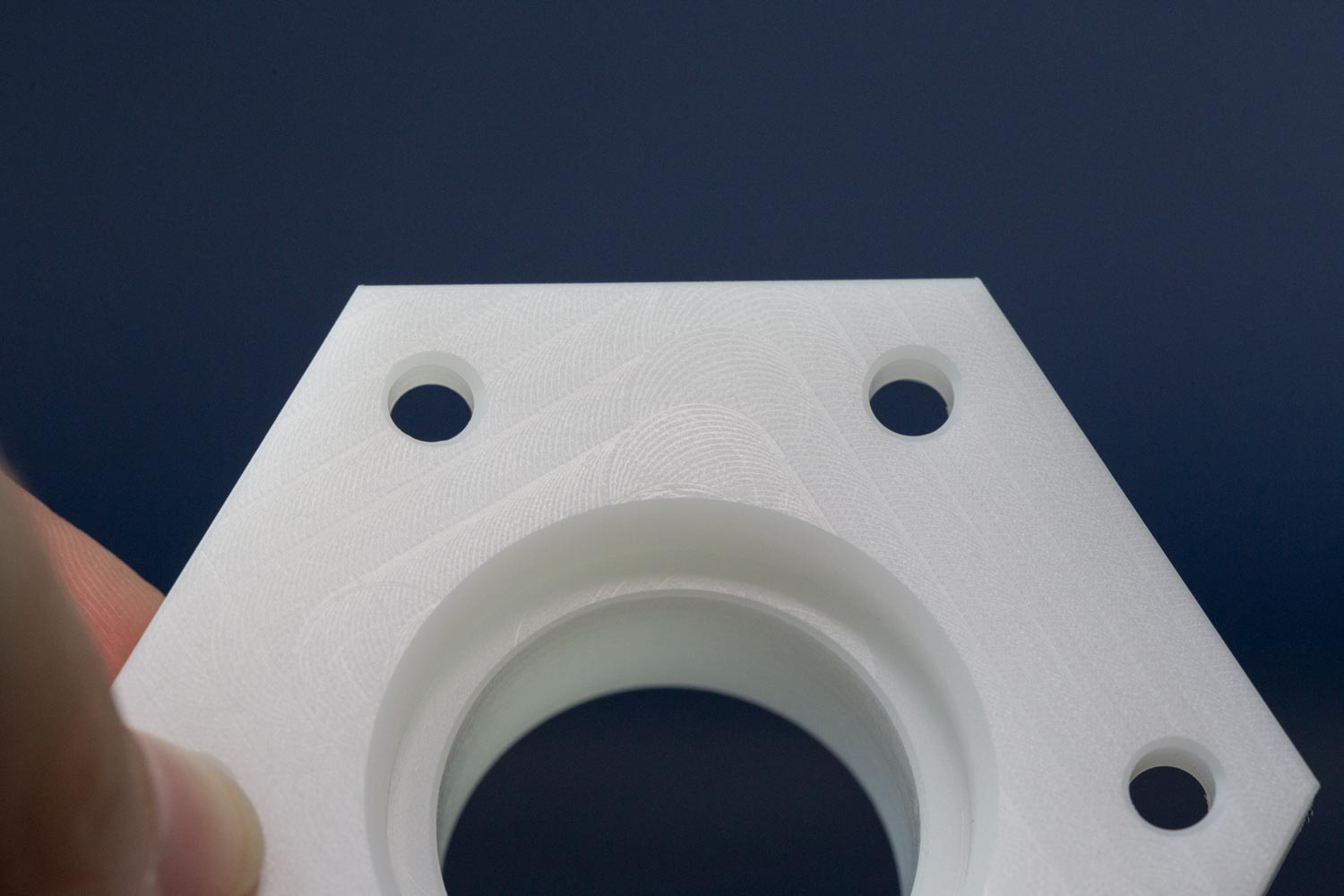
Holes
Threads
R 0.25mm
Recommended:
R 8
0.5 mm (for metals)
1.0 mm (for plastics)
Recommended:
0.8 mm (for metals)
1.5 mm (for plastics)
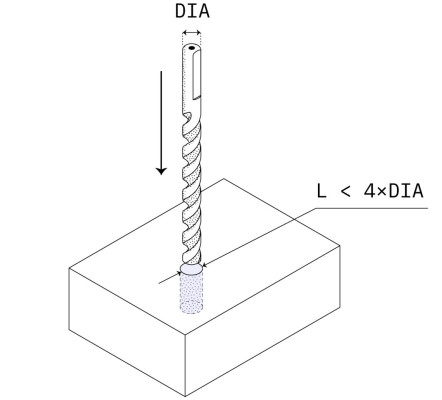
Diameter: Ø 0.5
Depth: 10 x diameter
Recommended:
Diameter:standard drill bit sizes
Depth: 4 x diameter
Recommended: M6 or larger